題目出處
難度
easy
個人範例程式碼 - Deque (比較進階),空間 O(N)
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
if not head:
return False
dq = deque([])
while(head):
dq.append(head.val)
head = head.next
return self.is_palindrome(dq)
def is_palindrome(self, dq):
while(len(dq)>=2):
if dq.popleft() == dq.pop():
continue
else:
return False
else: # if len(dq) <mark> 1, True or len(dq) </mark> 0, True
return True
最近在練習程式碼本身就可以自解釋的 Coding style,可以嘗試直接閱讀程式碼理解
算法說明
Deque 解 palindrome 的題目真的是無敵,但因為是比較進階的資料結構,也許不一定是面試想要看到的解
input handling
處理沒有 head 的情況,return False
Boundary conditions
控制 pointer 搜尋至 None
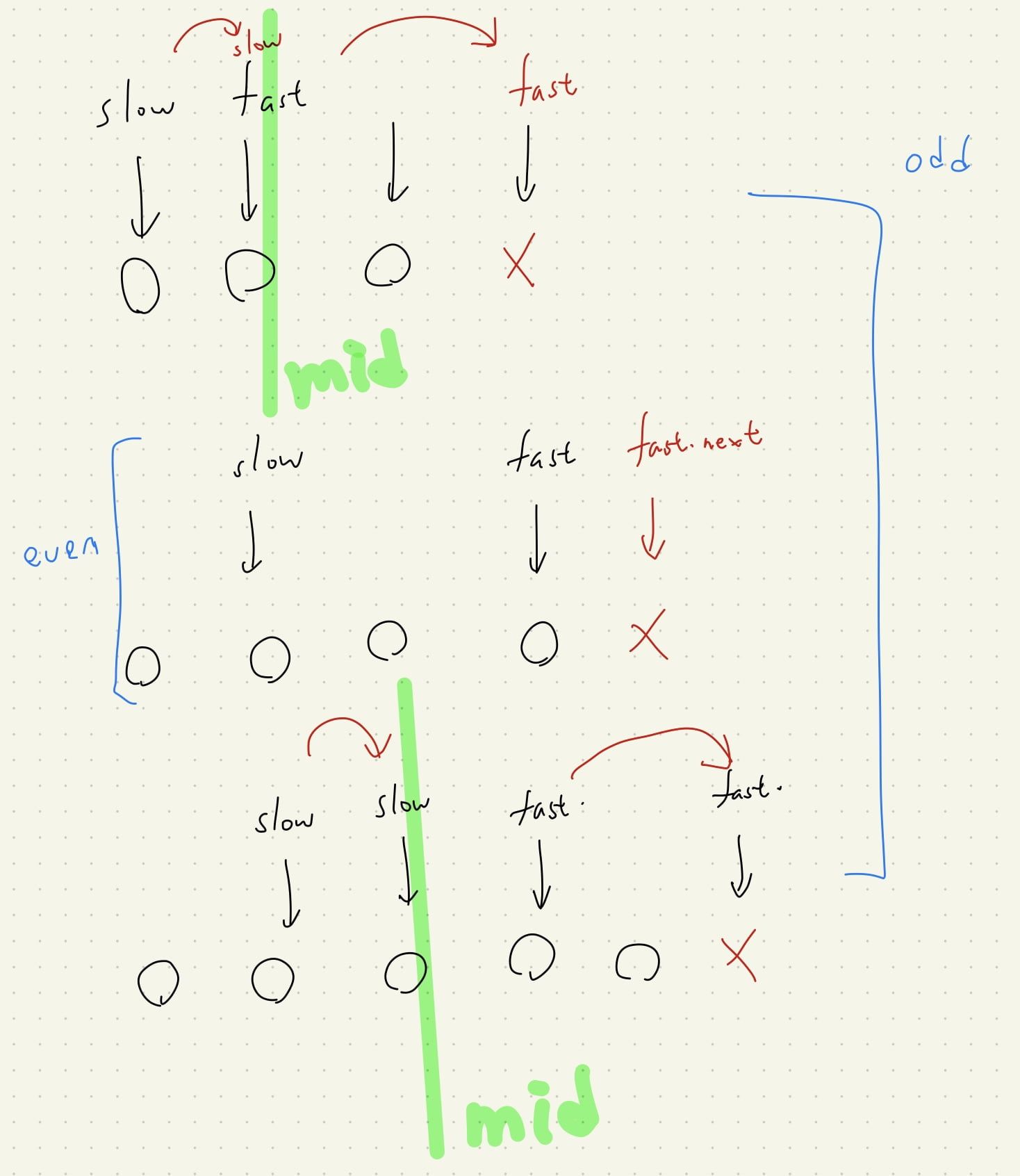
個人範例程式碼 - 同向 two pointer, 使用空間 O(N/2) stack
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
if not head:
return False
slow = head
fast = head.next
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
else:
if not fast:
return self.odd_case(head, slow, fast)
else: # not fast
return self.even_case(head, slow, fast)
def odd_case(self, head, slow, fast):
mid = slow
stack = deque([])
slow = slow.next
while(slow):
stack.append(slow.val)
slow = slow.next
# print(stack)
while(stack):
if head.val == stack.pop():
head = head.next
else:
return False
else:
return True
def even_case(self, head, slow, fast):
mid = slow
stack = deque([])
slow = slow.next
while(slow):
stack.append(slow.val)
slow = slow.next
# print(stack)
while(stack):
if head.val == stack.pop():
head = head.next
else:
return False
else:
return True
最近在練習程式碼本身就可以自解釋的 Coding style,可以嘗試直接閱讀程式碼理解
算法說明
我猜此題目最多會要求到把使用空間壓縮至 O(1),
這樣上面 Deque 的做法會因為空間 O(n) 而不能用。
如果要實現 O(1) 空間的話,
這題就可以考到 LinkedList 的反轉,同向 two pointer。
不過這邊求速度,就先不寫 LinkedList 的反轉,
使用 O(N/2) 空間的 stack 完成同樣的任務
input handling
處理沒有 head 的情況,return False
Boundary conditions
控制 slow, fast pointer 搜尋至 None,
注意結束條件的 fast and fast.next
個人範例程式碼 - 同向 two pointer,使用 reverse LinkedList 空間 O(1)
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
if not head:
return False
slow = head
fast = head.next
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
else:
if not fast:
return self.odd_case(head, slow, fast)
else: # not fast
return self.even_case(head, slow, fast)
def odd_case(self, head, slow, fast):
dummy = self.reverse(slow)
while dummy:
# print(dummy.val, head.val)
if dummy.val == head.val:
head, dummy = head.next, dummy.next
else:
return False
return True
def even_case(self, head, slow, fast):
dummy = self.reverse(slow.next)
while dummy:
# print(dummy.val, head.val)
if dummy.val == head.val:
head, dummy = head.next, dummy.next
else:
return False
return True
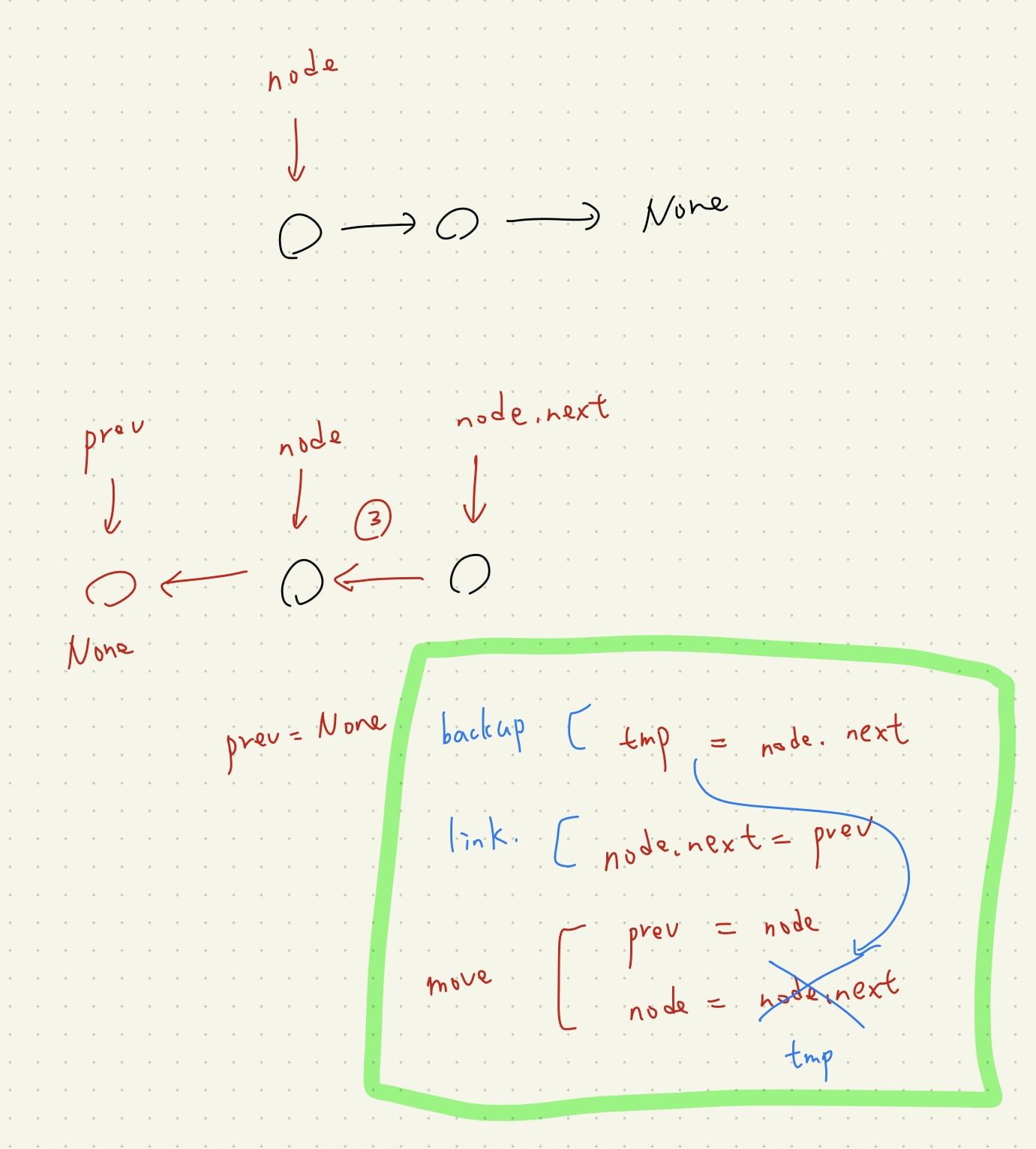
def reverse(self, node):
prev = None
while node:
tmp = node.next
node.next = prev
prev = node
node = tmp
return prev # prev <- node(None)
最近在練習程式碼本身就可以自解釋的 Coding style,可以嘗試直接閱讀程式碼理解
算法說明
同上 slow, fast 作法,但實現 O(1) 空間,利用 LinkedList 的反轉,同向 two pointer。
input handling
處理沒有 head 的情況,return False
Boundary conditions
控制 slow, fast pointer 搜尋至 None,
注意結束條件的 fast and fast.next