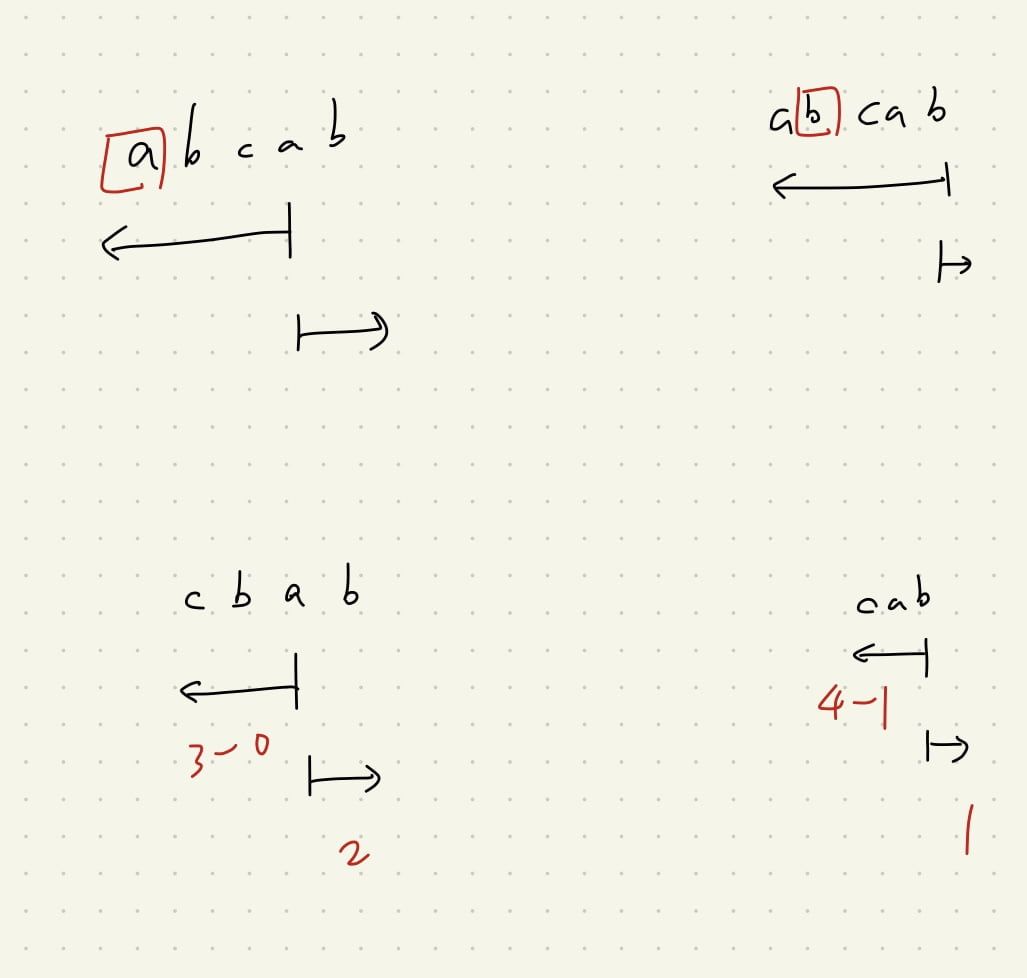題目出處
2262. Total Appeal of A String
難度
hard
個人範例程式碼 - dfs 解 (會 TLE)
class Solution:
def appealSum(self, s: str) -> int:
if not s:
return 0
self.ans = 0
# decide start
for i in range(len(s)):
self.dfs(s, i, i, set()) # decide end
return self.ans
def dfs(self, s, start, end, wordset):
# s[start:end+1] start~end
# end of recursion
if end >= len(s):
return
# define
if s[end] in wordset:
pass
else:
wordset.add(s[end])
self.ans += len(wordset)
# split
self.dfs(s, start, end+1, wordset)
最近在練習程式碼本身就可以自解釋的 Coding style,可以嘗試直接閱讀程式碼理解
算法說明
dfs 解法本身概念是對的,如果這題目最終要的是全部結果的窮舉,那一定是用 dfs 去組。
而這題目只需要數數量,因此 dfs 雖然方向對了,但可以透過一些手段加速。
input handling
如果 input 是 “",return 0 (題目沒有要求要處理)
Boundary conditions
控制 recursion 結束條件 if end >= len(s)
個人範例程式碼 - DP 解
class Solution:
def appealSum(self, s: str) -> int:
# dp[i] = dp[i-1] + newword
dp_contain_thisword = [0]
worddict = {}
for i, c in enumerate(s):
if c not in worddict:
dp_contain_thisword.append(dp_contain_thisword[-1] + i+1)
else:
dp_contain_thisword.append(dp_contain_thisword[-1] + i - worddict[c])
worddict[c] = i
# print(dp_contain_thisword)
return sum(dp_contain_thisword)
最近在練習程式碼本身就可以自解釋的 Coding style,可以嘗試直接閱讀程式碼理解
算法說明
原作者的說明:
我們將原來的題目視作,dp[i] = dp[i-1] + i 的格式
也就是說
- - 「包含此字的所有組合」=「包含前一個字的所有組合」+ 此字
- 而「全部組合」= 「包含此字的所有組合」的和
「包含此字的所有組合」=「包含前一個字的所有組合」+ 此字
- 正常情況,不重覆字就是「加上 idx+1」 (+1 是因為 0 開始)
- 有重複情況,我們可以視為,「重複之前的字母,都會少算 1 次」,因此需要多減去 prev[idx]
input handling
如果 input 是 “",return 0 (題目沒有要求要處理)
Boundary conditions
控制 for loop
個人範例程式碼 - 歸納法 解
class Solution:
def appealSum(self, s: str) -> int:
letter_contain_thisword = []
# 1*5, 2*4, 3*3 = left_len(a,ab,abc) * right_len(c,cd,cde)
# (a,ab,abc,abca) * (a, ab) = 4*2 -> (4-1)*2, since abca = bca (abca,bca,ca,a) = (bca,ca,a)
prev_idx = {}
for i, c in enumerate(s):
if c in prev_idx:
letter_contain_thisword.append((i - prev_idx[c])*(len(s)-i))
else:
letter_contain_thisword.append((i + 1)*(len(s)-i))
prev_idx[c] = i
return sum(letter_contain_thisword)
最近在練習程式碼本身就可以自解釋的 Coding style,可以嘗試直接閱讀程式碼理解
算法說明
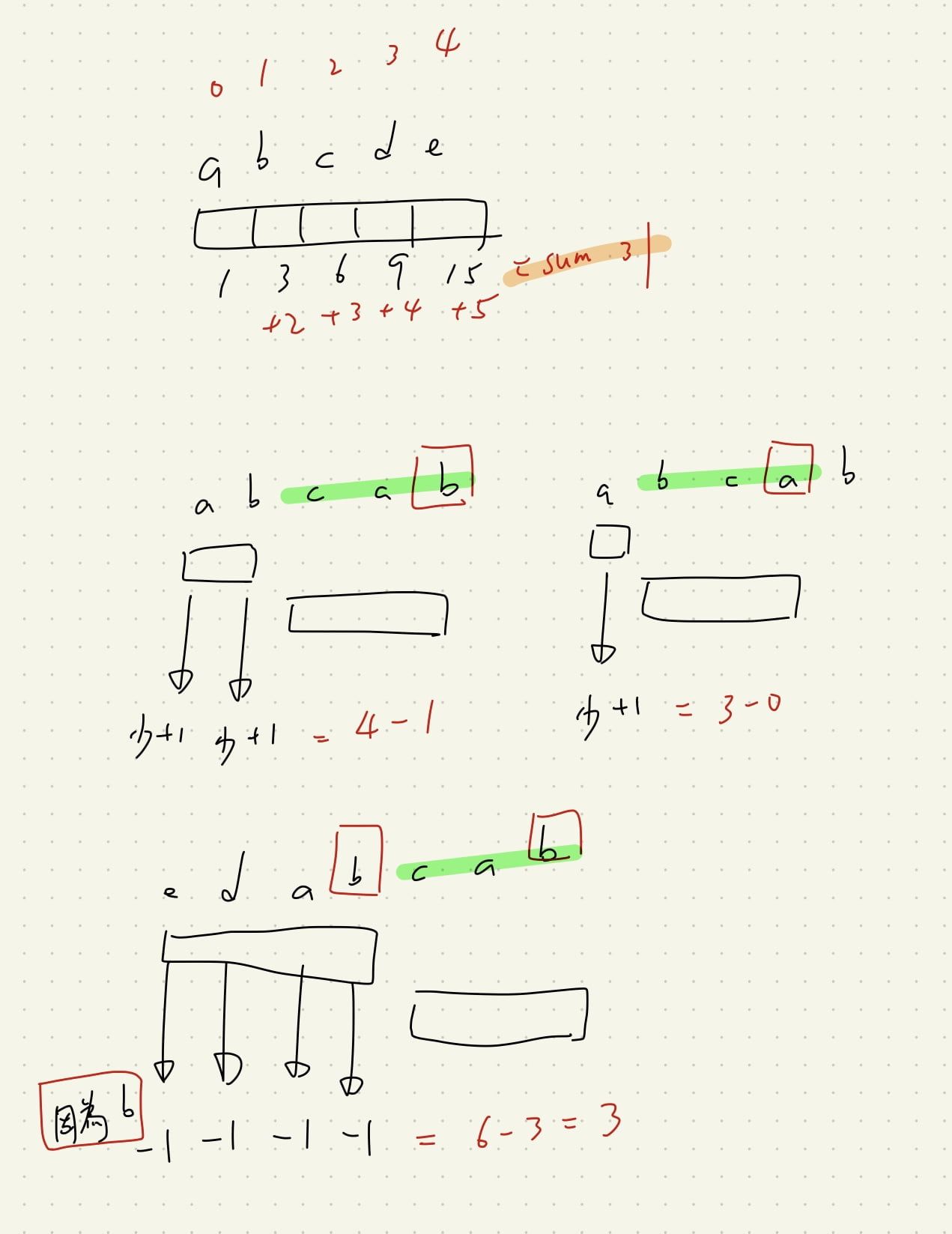
原作者的說明:
這個思維的出發點是「計算包含此字母的 substring 共有幾個」
正常情況
我們計算的是「包含此字的所有 substring」,因此
abcde = 15 + 24 + 33 + 42 + 5*1
(a) * (a,ab,abc,abcd,abcde)
(ab,b) * (b,bc,bcd,bcde)
(abc,bc,c) * (c,cd,cde)
重複情況
我們計算的是「包含此字的所有 substring」,因此
abcab = 15 + 24 + 3*3 + (3-0)*2 + (4-1)*1
(abca,bca,ca,a)(a,ab)
(abcab,bcab,cab,ab,b)(b)
因為重複的關係,因此 (abca,bca,ca,a) = (bca,ca,a),
只要是第一個 a 以前的都算在重複的範圍 (都要少算 1),因此可以推得 「i - prev[c]」
input handling
如果 input 是 “",return 0 (題目沒有要求要處理)
Boundary conditions
控制 for loop