前言
在機器學習的領域中,我們很常會需要用到 iou 的計算,
iou 全名為 intersection over union,
能替兩張圖形重疊的範圍提供一個參考分數,是一個相對具有參考意義的值。
本篇文章中也提供範例程式碼,
因為我自己也很常用XD,不時就會回來拿這段 function 去實作。
iou 的概念與公式
iou 基本上 = 兩矩形的交集 / 兩矩形的聯集
所以:
- 完全重合時:得到最大值 1
- 完全不重合時:得到最小值 0
- 部分重合:得到 0~1 範圍的值
以下為圖解
- 圖片引用自:https://blog.csdn.net/IAMoldpan/article/details/78799857
用 python 實作計算 iou 的 function
這邊先講一下我們的 input,為兩個 bbox,
兩個 bbox 都是一個具有四個值的 list,
分別儲存兩個矩形的 [x, y, w, h]。
要使用時請務必注意傳入格式!
註:底下的 function 有使用到 python 3.8 以後才有的 f-string 功能,
沒辦法正常運行的可以考慮用 format 的方式將 f-string 的部分重寫。
def get_iou(bbox_ai, bbox_gt):
iou_x = max(bbox_ai[0], bbox_gt[0]) # x
iou_y = max(bbox_ai[1], bbox_gt[1]) # y
iou_w = min(bbox_ai[2]+bbox_ai[0], bbox_gt[2]+bbox_gt[0]) - iou_x # w
iou_w = max(iou_w, 0)
print(f'{iou_w=}')
iou_h = min(bbox_ai[3]+bbox_ai[1], bbox_gt[3]+bbox_gt[1]) - iou_y # h
iou_h = max(iou_h, 0)
print(f'{iou_h=}')
iou_area = iou_w * iou_h
print(f'{iou_area=}')
all_area = bbox_ai[2]*bbox_ai[3] + bbox_gt[2]*bbox_gt[3] - iou_area
print(f'{all_area=}')
return max(iou_area/all_area, 0)
實驗與結果
這邊以 colab 進行實驗,因此有加一些額外的功能
(例如 colab 因為沒有視覺化視窗,不能用 cv2.imshow,改以用 matplotlib 套件代替)
colab 實驗連結 (可以自行遊玩):
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1wMb28P4RJDjmqyoV_znbbXZwEg_9C3sV?usp=sharing
colab 實驗用程式碼:
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import cv2
def show_img(img):
image_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
plt.imshow(image_rgb)
plt.show()
def draw_rectangle(img, bbox, color):
left_up = (bbox[0], bbox[1])
right_down = (bbox[0]+bbox[2], bbox[1]+bbox[3])
thickness = 1 # 寬度 (-1 表示填滿)
cv2.rectangle(img, left_up, right_down, color, thickness)
return img
def get_iou(bbox_ai, bbox_gt):
iou_x = max(bbox_ai[0], bbox_gt[0]) # x
iou_y = max(bbox_ai[1], bbox_gt[1]) # y
iou_w = min(bbox_ai[2]+bbox_ai[0], bbox_gt[2]+bbox_gt[0]) - iou_x # w
iou_w = max(iou_w, 0)
# print(f'{iou_w=}')
iou_h = min(bbox_ai[3]+bbox_ai[1], bbox_gt[3]+bbox_gt[1]) - iou_y # h
iou_h = max(iou_h, 0)
# print(f'{iou_h=}')
iou_area = iou_w * iou_h
# print(f'{iou_area=}')
all_area = bbox_ai[2]*bbox_ai[3] + bbox_gt[2]*bbox_gt[3] - iou_area
# print(f'{all_area=}')
return max(iou_area/all_area, 0)
shape = (100, 100, 3) # y, x, RGB
# 第一種方法,直接建立全白圖片 100*100
img = np.full(shape, 255).astype(np.uint8)
bbox_1 = [10, 20, 30, 40]
bbox_2 = [20, 30, 40, 50]
img = draw_rectangle(img, bbox_1, color=(0, 0, 255))
# show_img(img)
img = draw_rectangle(img, bbox_2, color=(0, 255, 0))
show_img(img)
print(get_iou(bbox_1, bbox_2))
此為,為了方便解釋,我們也加了畫矩形的功能在裡面。
實驗結果
看下圖,我們可以大概知道圖形的分布
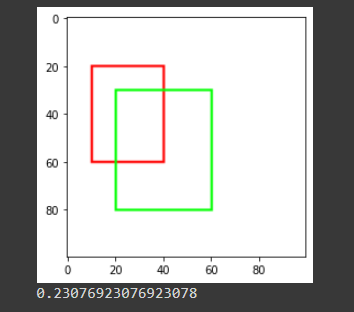
- 首先是紅框 (bbox_1),面積為 30*40=1200
- 再來是綠框 (bbox_2),面積為 40*50=2000
- 紅綠框交疊部分 ,面積為 (40-20)*(60-30)=600
- 紅綠框聯集,面積為 1200+2000-600 = 2600 (兩個相加後,扣掉重複部分)
得到結果 600/2600 = 0.23076923076 (就是我們上面最後印出來的結果囉!)
程式碼詳細說明
基本上我們在做的事情就是
- max(x1, x2) ,得到交集的左邊 x
- max(y1, y2) ,得到交集的上面 y
- min(x1+w1, x2+w2) ,得到交集的右邊 x
- min(y1+h1, y2+h2) ,得到交集的下面 y
就可以計算囉!
但也是會有沒考慮到的地方(不是特例):

上面的圖,如果照我們的公式,
我們取
- max(x1, x2) ,得到圖中右邊的箭頭 x
- min(x1+w1, x2+w2) ,得到圖中左邊的箭頭 x
結果算出來就是負的了…
發現潛在的計算問題了嗎?
沒錯,也就是說,當我們發現 min(x1+w1, x2+w2) < max(x1, x2) 時 (相減會負),
或是 min(y1+h1, y2+h2) < max(y1, y2) 時 (相減會負),
我們就要讓他答案直接為 0 ! (也要避免負負得正!)
這就是為什麼我們要做下面 max 的原因。
iou_w = max(iou_w, 0)
iou_h = max(iou_h, 0)
關於最後的計算
你可能會想問,為什麼最後還要做以下的 max?
return max(iou_area/all_area, 0)
其實只是為了再次避免我們算出負的,但基本上有上面那一點的預防,
我們其實這個避免 0 的功能應該是用不到的XD,
但寫了也是保險!
想看 C++ 計算 iou 方法,可見我的另外一篇文
https://wongwongnotes-github-io.pages.dev/cplusplus/opencv-cpp-iou/
